The Science Behind Berberine
Berberine has recently taken social media by storm for its potential role in supporting healthy weight management and metabolic wellness. What makes it so intriguing is its natural ability to influence key pathways in the body that regulate fat metabolism, energy balance, and blood sugar levels. As conversations around natural health alternatives grow, many are turning to berberine not just for its impact on weight, but also for its broad range of health benefits.
So, what makes berberine so unique, and why is it being celebrated as more than just another wellness trend? Let’s explore what this golden compound is, how it works, and the science behind its holistic benefits beyond weight management.
What is Berberine?
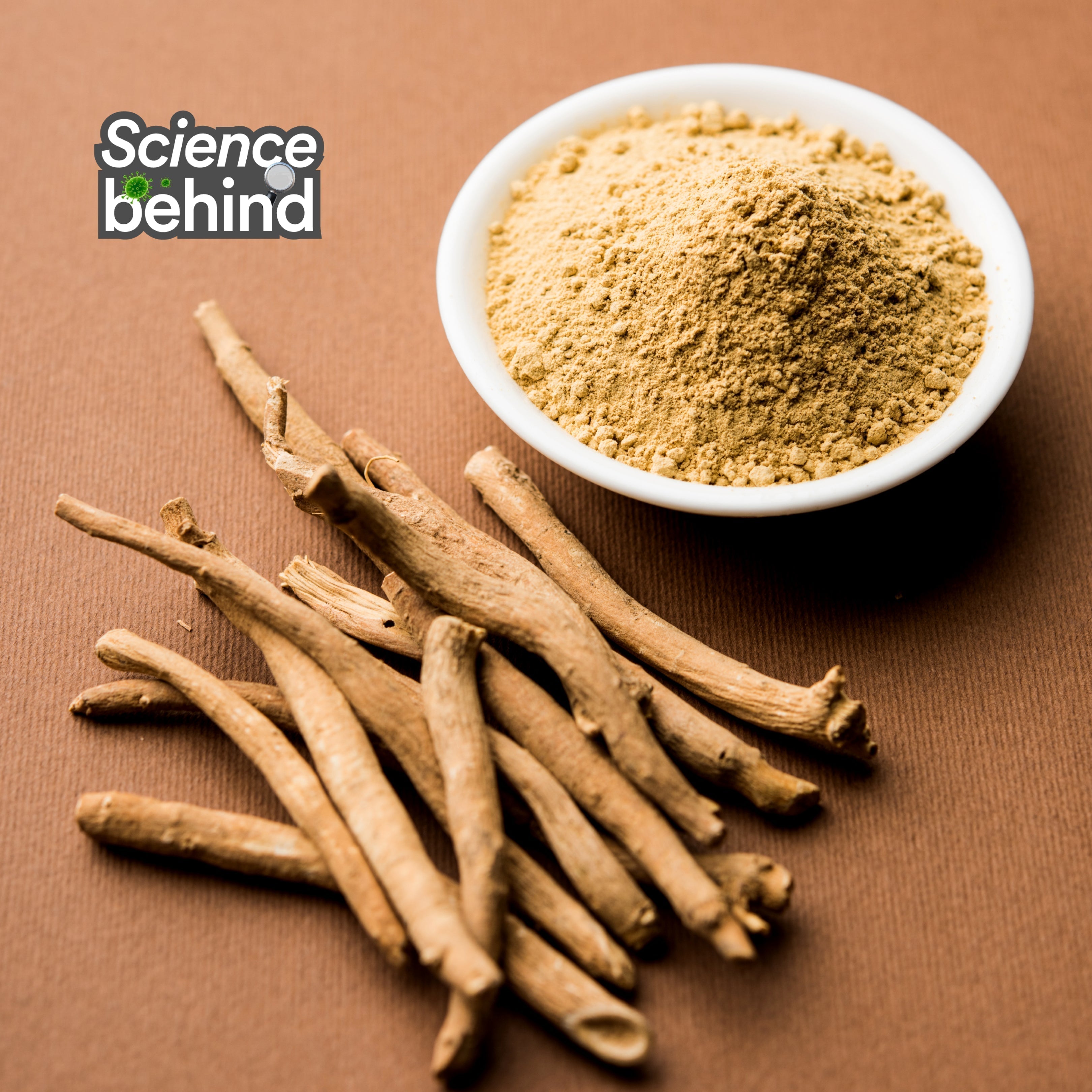
Berberine, also known as berberine HCl, is a natural compound found in the roots and stem bark of Berberis species, such as Berberis aristata. It is yellow in colour, and plants containing berberine have historically been used as a dye, particularly for colouring wool. This bright yellow alkaloid (a naturally occurring plant chemical) has a long history of use in traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine.
Revered for its wide range of health benefits, berberine was traditionally used as a remedy for digestive issues, infections, and skin conditions. Today, it is gaining popularity as a natural supplement supported by modern scientific research, thanks to its ability to activate the AMPK pathway, often called the "metabolic master switch/master regulator."
How does Berberine work?
Berberine is one of the few compounds known to activate AMPK-Adenosine Monophosphate activated Protein Kinase (adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase), a vital enzyme that plays a key role in regulating energy balance and metabolism. By activating AMPK, berberine helps improve glucose metabolism, reduce fat storage, and enhance overall cellular health.
To learn more about AMPK refer to this blog.
Benefits of Berberine

Atherosclerosis and Heart Health
Atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up inside the artery walls, can narrow and harden the arteries, affecting blood flow and raising the risk of severe health issues. Berberine may help by reducing the adhesion of monocytes (a type of white blood cell) to the endothelium—the initial step in plaque formation. This action can support heart health and circulation.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Type 2 diabetes is often linked to insulin resistance and damage to the pancreas’s β-cells, which produce insulin. Berberine has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and support the repair of damaged or exhausted β-cells, aiding in healthier blood sugar levels and better glucose metabolism.
PCOS and Hormonal Balance
Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) often experience high insulin levels, which can cause the ovaries to produce excess androgens, such as testosterone. Berberine, through the activation of the AMPK pathway, helps improve insulin signaling, thereby enhancing glucose uptake and improving hormone balance in women with PCOS.
Fat Metabolism
Berberine is one of the few natural compounds known to activate AMPK, which plays a vital role in fat metabolism. Activation of AMPK promotes fat burning in the mitochondria, increases the breakdown of triglycerides, and reduces fat accumulation in the body.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excess fat in the liver, even in individuals who don’t consume much alcohol. Research suggests that Berberine can be effective in managing NAFLD. Studies have shown that Berberine significantly reduces fat storage in the liver and supports liver health by positively impacting the gut microbiota and reducing liver fibrosis.
Gut Health
Berberine is beneficial for gut health, thanks to its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-diarrheal properties. It effectively combats a range of pathogens—bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites—helping to reduce harmful microorganisms in the gut. Additionally, berberine’s anti-inflammatory effects can ease gut inflammation linked to conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), alleviating symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Common ways Berberine is used
Berberine is a versatile ingredient with a range of applications in health and wellness. Here are some of the most common ways it's used:
-
Supplements: Berberine is widely available in the form of capsules, tablets, or powders. It is primarily used in supplements for its various benefits. Supplements are often the most popular way to consume Berberine due to their ease of use and precise dosing.
-
Teas: Traditionally, Berberine has been used in herbal teas, particularly in Chinese medicine. These teas are often brewed from Berberine-rich plants like Berberis vulgaris (Barberry) and are believed to support digestion and provide antioxidant benefits.
Recommended dosage
Berberine is generally considered safe when consumed in doses up to 1,500 mg per day, divided into 2-3 smaller doses. Spreading the dosage throughout the day helps maintain consistent levels in the body, ensuring optimal absorption and effectiveness.
Potential side effects and safety
-
Side Effects: Some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort when taking Berberine in high doses. Starting with a lower dose can help minimize these effects.
-
Safety for Long-Term Use: Berberine is generally considered safe for long-term use when taken at the recommended dosage. However, it's advised to take periodic breaks or consult with a healthcare provider for extended use.
-
Who Should Avoid It: Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take Berberine. Additionally, caution is needed when combining Berberine with certain antibiotics, such as azithromycin, as it may have an impact on heart health.
Choosing the right Berberine supplement
Because Berberine has low oral bioavailability, selecting high-strength supplements can enhance its absorption and effectiveness. Origins Nutra Berberine supplement is a high-strength formula with 99% pure Berberine, offering higher bioavailability. Made in a pharma-grade facility and verified through third-party testing, it ensures quality, purity, and potency. Choosing a supplement like this, which clearly states its Berberine source (such as Berberis aristata) and adheres to rigorous quality standards, can be your right choice for better results and peace of mind.
Conclusion: Is Berberine Right for You?
Berberine is a natural compound with a history of traditional use and strong backing from modern research. Its ability to support healthy blood sugar levels, improve cardiovascular health, balance hormones, and aid in fat metabolism makes it a versatile choice for enhancing overall well-being. It’s important to choose the right form, maintain the proper dosage, and consider your unique health needs to maximize its benefits.