What Is GLP-1? 7 Natural Ways to Boost This Hormone
GLP-1 seems to be everywhere lately, on social media, in wellness reels, weight loss ads, even at your doctor’s office. You’ve probably heard claims like “GLP-1 is the future of fat loss” or “Boost GLP-1 naturally with these foods,” and while it all sounds promising, it can also feel overwhelming and overhyped.
If you’ve been wondering what GLP-1 really is, how it works in your body, and whether you actually need injections or can support it through lifestyle, you're not alone. In this guide, we’ll break it all down, simple, and science-backed. So, you can understand GLP-1 and how to naturally support it without getting lost in the noise.
What is GLP-1, anyway?
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is an incretin hormone which means it is produced in your gut. Think of it as a helper that works after you eat. Here’s how it helps:
-
Help your body use insulin, which keeps your blood sugar in balance
-
Make you feel full and stop you from overeating
-
Tell your brain that you’ve had enough food

So, GLP-1 plays a major role in controlling your hunger and helping your body process food properly. Because of these effects, GLP-1 is a big focus in type 2 diabetes treatment and weight management research.
Why Boosting GLP-1 Naturally Matters
While your body does produce GLP-1 on its own, it often doesn’t make enough to keep up with modern dietary patterns, stress, and poor gut health. Plus, the natural hormone breaks down quickly, within minutes, so its effects don’t last long unless consistently supported.
You’ve probably heard of GLP-1 medications like Semaglutide or Tirzepatide, which are popular for treating type 2 diabetes and weight management. However, these medications come with some side effects, like nausea and vomiting.
That's why exploring natural ways to stimulate GLP-1 is valuable especially if you want to support your body’s own systems safely and sustainably.
7 Natural ways backed by science to increase GLP-1
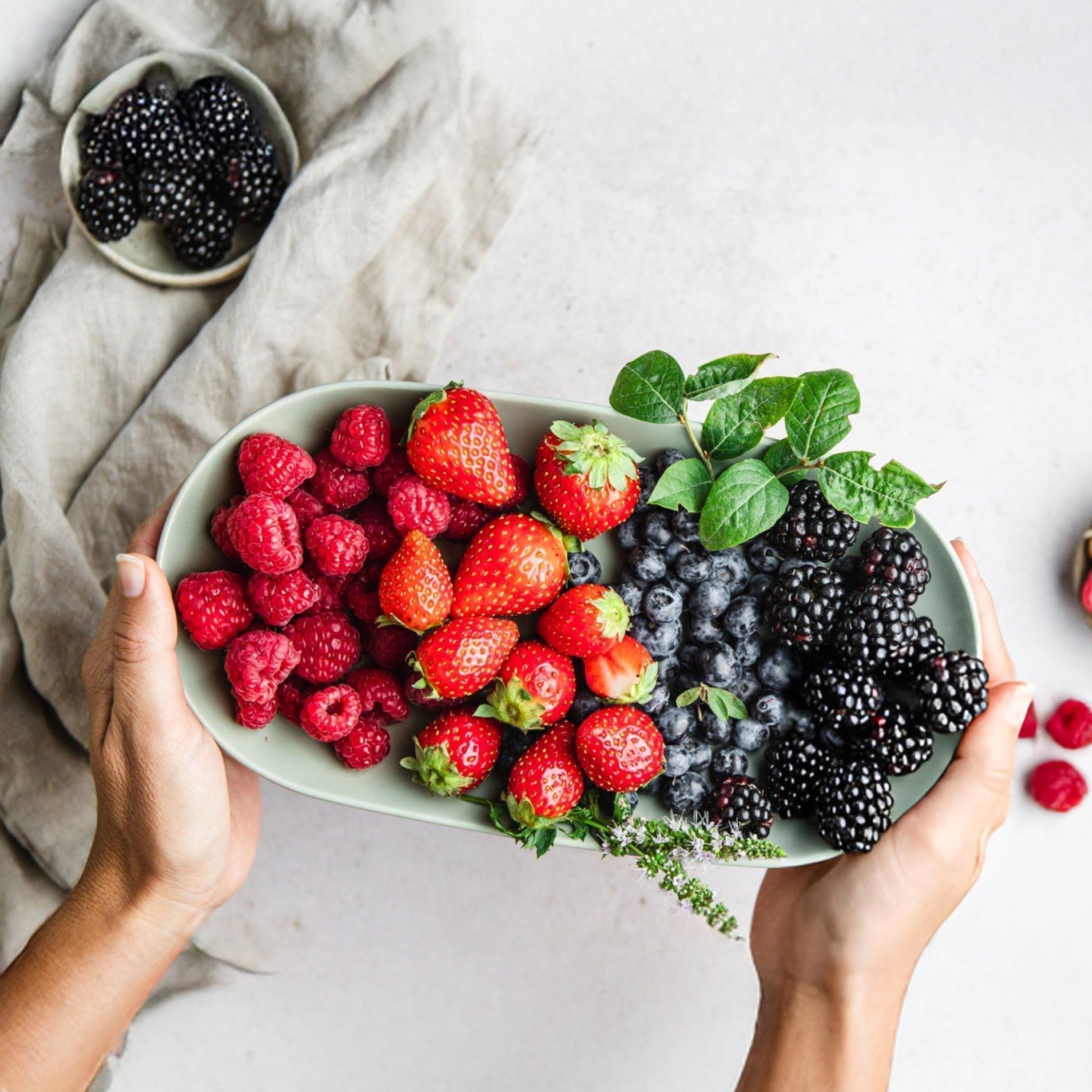
1. Eat More High-Fiber Foods to boost GLP-1
Eating foods that are high in fiber is one of the easiest ways to increase GLP-1. Fiber doesn’t get digested directly by your body, but the bacteria in your gut break it down. This process produces substances that help trigger GLP-1 production. When your gut is healthy, your GLP-1 levels go up, helping you feel full and better manage your metabolism.
How Fiber Triggers GLP-1:
Think of fiber as "food" for your gut bacteria. When your gut bacteria eat it, they produce short-chain fatty acids, which tell your body to make more GLP-1. This helps control hunger and keeps blood sugar in check.
Fiber-Rich Foods:
-
Whole grains like oatmeal and brown rice
-
Beans and lentils
-
Fruits like apples and bananas
-
Vegetables like broccoli and carrots
Why It Works: Fiber improves your gut health, which leads to more GLP-1, helping you feel satisfied and control your blood sugar
(Ref: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10790698/#ack1)
2. Add More Protein to Your Meals
Eating protein-rich diets is another way to boost GLP-1. When your body digests protein, it releases certain building blocks (called amino acids) that help trigger GLP-1 production in your gut. This means eating more protein can help you feel full and also help with managing blood sugar.
How protein triggers GLP-1 :
When you eat protein, your body sends a signal to release more GLP-1, which makes you feel full longer and helps control your blood sugar levels.
Protein-Rich Foods:
-
Eggs
-
Chicken, turkey, or fish (like salmon)
-
Beans and lentils
Why It Works: Protein helps release GLP-1, so you feel fuller longer and your blood sugar stays in a healthy range.
(Ref: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2161831322005208)
3. Eat Omega-3 Fats to Boost GLP-1
Healthy fats, like omega-3 fatty acids, are good for your body in many ways, and they can also help increase GLP-1. These healthy fats send signals in your gut that tell it to produce more GLP-1, which helps manage appetite and blood sugar.
How omega-3’s triggers GLP-1:
Omega-3 fats are like a signal to your body that says, "Make more GLP-1!" This helps keep your metabolism working smoothly and helps with fat burning.
Omega-3-Rich Foods:
-
Salmon and other fatty fish
-
Flaxseeds and chia seeds
-
Walnuts
Why It Works: Omega-3s help your gut work better and send signals to make more GLP-1, which keeps your metabolism balanced.
( Ref: https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=54963 )
4. Get Moving: Exercise Increases GLP-1
When you exercise, especially through muscle contraction (like when you lift weights or do cardio), your body produces more GLP-1. Regular exercise also helps improve how your body handles blood sugar and burns fat.
How exercise triggers GLP-1 :
When you exercise, your muscles release signals that tell your gut to produce more GLP-1. This helps regulate hunger and keeps your blood sugar in check.
Best Exercises for GLP-1:
-
Walking or cycling
-
Weightlifting or strength training
Why It Works: Exercise activates your muscles to release signals that increase GLP-1, which helps balance your hunger and metabolism.
( Ref: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6107470/ )
5. Sleep Helps GLP-1 Production
Getting enough sleep is critical for hormonal balance. If you don’t sleep well, it can mess up your hormones, including GLP-1. When you get proper rest, your body can produce the right amount of GLP-1, helping you feel satisfied and manage blood sugar better.
How sleep triggers GLP-1:
Sleep acts like a reset button for your hormones. When you sleep well, your body can make more GLP-1, which helps with hunger control and metabolism.
Why It Works: Sleep helps keep your hormones in balance, making it easier for your body to produce the right amount of GLP-1.
( Ref: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3697408)
6. Gut Health is Key to Boosting GLP-1
A healthy gut is essential for GLP-1 production. The better your gut health, the more GLP-1 your body can produce. This is why maintaining a healthy gut microbiome (the good bacteria in your gut) is important for regulating your appetite and metabolism.
How gut health triggers GLP-1:
When your gut bacteria are happy and healthy, they send signals to increase GLP-1 production, which helps manage hunger and blood sugar. (Ref:https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5378938/ )
Gut-Healthy Foods:
-
Yogurt and kefir (contain probiotics)
-
Prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and asparagus
-
High-fiber foods
Why It Works: A balanced gut microbiome helps your body make more GLP-1, improving appetite control and blood sugar management.
7. Berberine: A Natural GLP-1 Booster
Berberine, a plant-derived compound, is gaining attention for its ability to increase GLP-1 levels naturally.
How Berberine triggers GLP-1:
Studies suggest that berberine helps stimulate the secretion of GLP-1, aiding in better appetite control and glucose metabolism. This makes it a valuable supplement for people looking to enhance GLP-1 without using medications.
Why It Works: Berberine influences gut health and increases GLP-1 production, supporting weight management and blood sugar balance.
( Ref: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9452888/#)
Conclusion: Small Changes, Big Impact
You don’t need expensive medications to support your body's GLP-1 hormone naturally.
By eating more fiber, protein, and healthy fats, moving daily, sleeping better, feeding your gut, and managing stress, you can give your metabolism a powerful boost.
Start with one or two changes today, your body (and future self) will thank you.
FAQ’s: Everything You Need to Know About GLP-1.
-
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a hormone made in the gut that helps regulate blood sugar by boosting insulin, lowering glucagon, and slowing digestion.
-
What are GLP-1 medications?
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic natural GLP-1. They are used to lower blood sugar, support weight loss, and manage type 2 diabetes.
-
What is GLP-1? Is it a hormone or a medicine?
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a natural hormone produced in the gut. It helps regulate blood sugar, slows stomach emptying, and reduces appetite after meals. While GLP-1 itself is not a medication, several drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists are designed to mimic its effects for treating type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss.
-
Is GLP-1 better than metformin?
GLP-1 agonists may offer stronger weight loss and blood sugar control benefits compared to metformin, but both are effective depending on individual needs.
-
Which GLP-1 is taken daily?
Liraglutide (Victoza) is a daily GLP-1 injection often used for diabetes and weight management.
-
How can you naturally activate GLP-1?
You can boost GLP-1 naturally by eating fiber-rich foods, healthy fats, lean proteins, exercising regularly, managing stress, and getting good sleep.
-
Is GLP-1 better than insulin?
GLP-1 medications are better for post-meal glucose spikes and weight loss, while insulin is better for overall blood sugar control in severe cases.
-
Is GLP-1 a hormone?
Yes, GLP-1 is a natural incretin hormone that helps the body manage blood sugar and appetite.
-
What is the mechanism of action of GLP-1?
GLP-1 increases insulin release, decreases glucagon, slows stomach emptying, and enhances satiety to control blood sugar.
-
Can GLP-1 medications be used for PCOS?
Studies suggest GLP-1 agonists can help women with PCOS by improving insulin sensitivity and aiding weight loss.